Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia – Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
by
13th January 2022
9 minutes read
Gynecomastia, a condition that affects men and boys, has long been shrouded in silence and misunderstanding. It’s a topic that many shy away from discussing, yet for those who experience it, the physical and emotional impact can be profound. In this blog, we aim to shed light on this often-overlooked condition, offering knowledge, support and hope to those affected.
What is Gynecomastia?
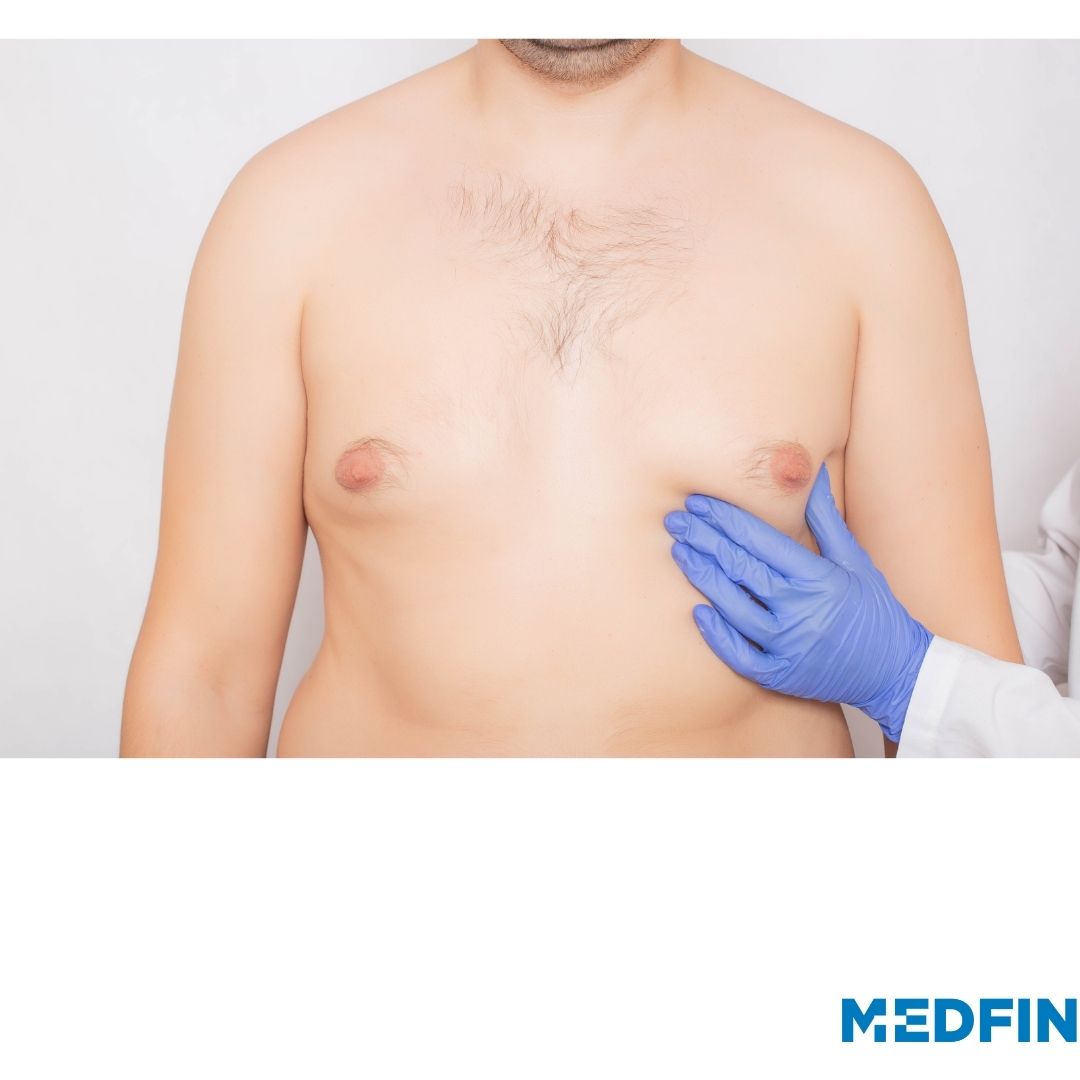
Gynecomastia is a medical condition characterized by the enlargement of the breast tissue in males. This condition can result in the development of swollen or overgrown breasts in men or boys. While it is not typically a serious health issue, it can lead to low self-esteem and body image concerns. Gynecomastia is often caused by an imbalance of hormones, specifically an increase in estrogen (female sexual hormone) relative to testosterone (male sexual hormone). There are various factors that can contribute to this hormonal imbalance, including puberty, certain medications, medical conditions, and lifestyle factors like excessive alcohol or drug use. The gynecomastia treatment plan would made based on the cause and other individual factors. Let’s understand the condition in detail.
Symptoms
Enlarged breast/s is the most common sign of this condition. Other gynecomastia symptoms include rubbery or firm breasts, and breast bud on just one or both sides. Breast buds are a common phenomenon in adolescent boys when they are in puberty. Apart from this the patient may experience breast tissue swelling and tenderness. It may be a result of obesity as well.
Causes of Gynecomastia
Here are the common causes of gynecomastia:
1. Hormonal Imbalance:
An imbalance between estrogen (female sex hormone) and testosterone (male sex hormone) is one of the most common causes of gynecomastia. When there is an increase in estrogen relative to testosterone, it can lead to breast tissue growth. This imbalance can be temporary, as seen during puberty, or chronic due to various factors, including aging, obesity, or certain medical conditions.
2. Puberty:
Gynecomastia is a relatively common occurrence during puberty. As hormone levels fluctuate, it is not unusual for adolescent boys to experience temporary breast tissue enlargement. In most cases, this resolves on its own as hormone levels stabilize.
3. Medications:
Certain medications can cause gynecomastia as a side effect. These medications include:
- Anti-androgens: Drugs used to treat prostate cancer.
- Anabolic steroids: Often used by bodybuilders and athletes.
- Medications that affect hormone production or metabolism, such as some antipsychotics or drugs used to treat ulcers or heart conditions.
4. Underlying Medical Conditions:
Some medical conditions can disrupt the hormonal balance and lead to gynecomastia. These conditions may include:
- Hypogonadism: A condition in which the testes do not produce enough testosterone.
- Hyperthyroidism: Overactive thyroid gland.
- Tumors: Some tumors in the testes, adrenal glands, or pituitary glands can produce hormones that affect the balance between estrogen and testosterone.
5. Lifestyle Factors:
Lifestyle choices can also contribute to gynecomastia. These factors may include:
- Excessive alcohol consumption.
- Recreational drug use, including marijuana and certain stimulants.
- Obesity: Excess body fat can lead to an increase in estrogen production and a hormonal imbalance.
It’s important to note that gynecomastia can vary in severity, and the underlying cause may differ from one individual to another.
How is Gynecomastia Diagnosed?
Your healthcare professional may use the following methods to diagnose gynecomastia:
- Medical History: The doctors will record your medical history, which includes your current symptoms and previous medical and personal history.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination will be conducted in order to assess the size, consistency, and tenderness of the breast tissue.
- Blood tests: A few blood tests may be prescribed in order to assess hormone levels, especially testosterone and estrogen.
- Imaging Studies: This includes tests such as mammograms or breast ultrasounds that will help confirm the diagnosis.
A timely and accurate diagnosis is crucial for determining the cause and developing an appropriate treatment plan for gynecomastia.
Gynecomastia – Treatment
Observation and Lifestyle Modification:
For some individuals, gynecomastia may resolve without any specific treatment. In such cases, it may be advisable to monitor the condition and make lifestyle changes, such as weight loss, which can help reduce excess fat contributing to the appearance of gynecomastia.
Medications:
- Hormone-altering medications can be prescribed to manage gynecomastia in certain cases, particularly when it’s related to hormonal imbalances. Common medications include:
- Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs): Examples include tamoxifen and raloxifene, which can help block the effects of estrogen on breast tissue.
- Aromatase Inhibitors: These drugs, like anastrozole, work to reduce estrogen production in the body.
- Danazol: An androgen that can help reduce breast tenderness and pain.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is often recommended for individuals with persistent or severe gynecomastia. Two main surgical techniques are employed:
- Liposuction: This procedure involves the removal of excess fat from the breasts, which can be effective for cases where excess fat is the primary concern.
- Glandular Tissue Removal: When glandular tissue is a significant factor, surgical removal of the glandular tissue may be necessary. In some cases, skin may also need to be excised to provide a smoother contour.
Combination Therapy:
In some cases, a combination of medications and surgery may be recommended to address both the hormonal and physical aspects of gynecomastia.
The choice of treatment will depend on individual factors, including the underlying cause, the size and severity of gynecomastia, and the patient’s preferences.
Causative factors of gynecomastia
Based upon age, classification of causes for gynecomastia can be as follows:
- New-borns: This condition can arise in new-borns by oestrogen from the mother. The breast buds are not just common in babies, but they also go away within 6 months of age.
- Preteen boys: In preteen boys, the breast buds may appear during puberty. They go away within a year, but may last two years as well. Another factor for gynecomastia in preteens is oestrogen-producing tumour.
- Adult males: Usually the causes in adults are overactive thyroid, cirrhosis of the liver, lung or liver cancer, or hormonal issues. The hormonal problems include cancer of the adrenal glands, pituitary gland or testicles. It can be alcohol, methamphetamine, marijuana and heroin causing gynecomastia. In older males, hormonal changes are the major cause.
Obesity is yet another of the most common causes of gynecomastia. Heredity and obesity both can also influence the condition.
There can be some other factors as well. It can be an intake of certain medicines such as steroids, antiandrogen drugs, anti anxiety medicines, medicines to treat ulcers and epilepsy, and chemotherapy drugs.
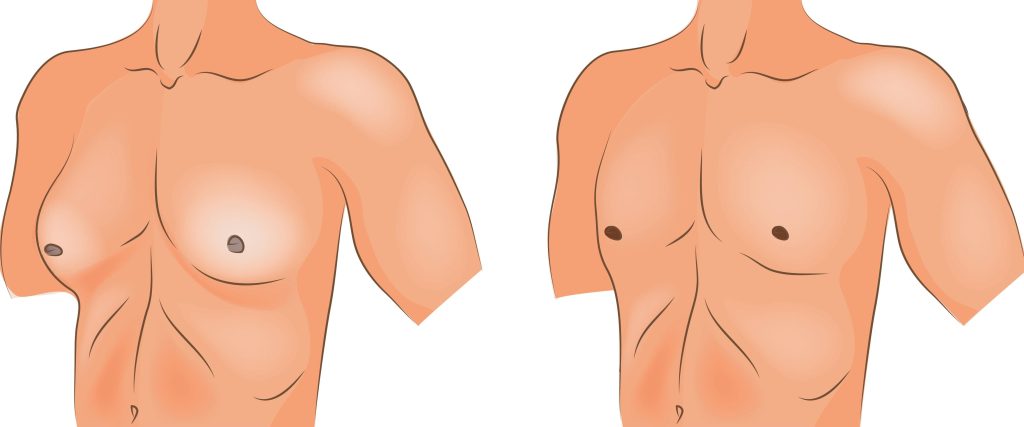
How to diagnose gynecomastia?
The diagnosis can be from one’s medical history and physical exam. Tests are usually not necessary. When the breast lump is large enough, tender, hard/fixed or one-sided, a biopsy may be the solution.
Any man with a one-sided breast lump should visit a doctor. He may let the doctor know if any close relative has had breast cancer in the past. Lastly, when there’s a concern about cancer, a biopsy or surgery are the solutions.
The healthcare provider may diagnose using blood tests, urinalysis and mammogram. It is also necessary to make sure the breast lump is due to overgrowth of the glandular tissue and not because of excess fat tissue.
Treatment – How to get rid of gynecomastia?
Questions such as how to reduce gynecomastia, or how to get rid of gynecomastia during puberty, are quite common. Here’s how-
Gynecomastia in teens and babies generally goes away without treatment. When caused because of medicines and diseases, stopping the same will often cure the condition. When the cause is hormonal changes, hormonal treatment is enough.
People want to know can gynecomastia go away with exercise. Diet and exercise can surely help reduce total body fat, thereby reducing the chest size too. Surgery comes out as the last option after all these treatment options fail to work.
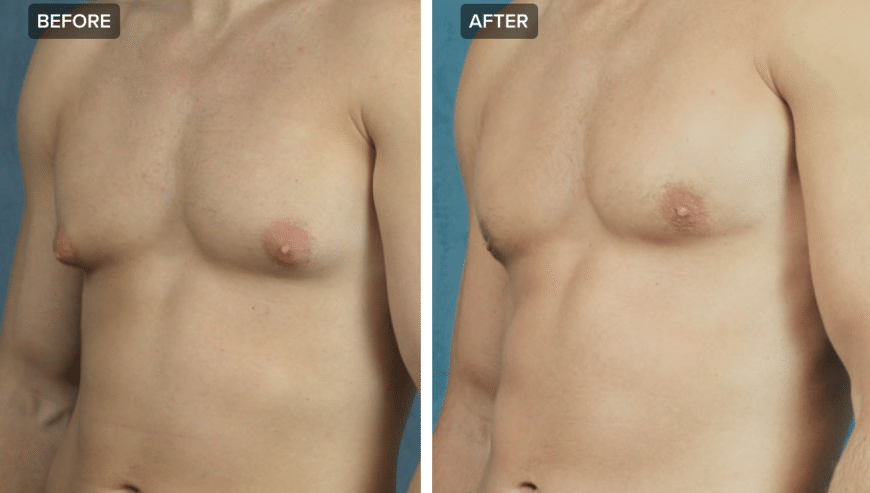
Gynecomastia surgery
The surgery includes removal of the excess glandular tissue and reshaping of the chest in position. It begins with anaesthesia – general, spinal or local anaesthesia. Anaesthesia type will depend upon factors such as extent of growth, age and size of incision. Here are the two different surgical procedures for this kind of plastic surgery:
- Suction lipectomy: This form of liposuction allows for the tapering of the edges of tissue. It does not cause side effects. When the condition is critical, an open surgical procedure may be the right option. In this case, there will be an incision into the breast tissue to remove the excess tissue.

- Endoscopic surgery: Here, the doctor uses a small and flexible tube with light and camera. He examines the inside of the breast and removes the tissue without making a large incision.
Post liposuction
After liposuction, the skin tightens itself when there’s good elasticity. This is generally with younger men due to better retraction of skin. However, some are left with loose skin even after the surgery. Therefore, going forward with an auxiliary procedure, once the blood flow is re-established, the doctor removes a donut-shaped skin piece from around the areola. He finally closes it with purse string sutures.
Post the surgery, the patient will need to visit the doctor multiple times for bandage replacement and further assessment. The doctor will direct him about the post-surgical care methods so as to cure the wound and recover completely.
We at Medfin , the Surgery expert team offers you access to latest and advanced treatment for elective surgeries at most affordable costs. Our Personal Medfin assistants answer all your concerns related to surgery and ensure that your needs are met in your entire medical journey.
Cost of Gynecomastia Treatment
The cost of gynecomastia treatment in India can vary widely depending on several factors, including the specific type of treatment, the city or region where the procedure is performed, the qualifications and experience of the healthcare provider or surgeon, and the facilities used. Whereas the cost of minimally invasive procedures such as liposuction can range from ₹30,000 to ₹1,00,000 INR or more, Gynecomastia surgery can range from ₹60,000 to ₹2,00,000 INR or more. To obtain an accurate cost estimate, it’s recommended to consult with experienced healthcare providers or surgeons in your city and discuss the specific details of your case.
[su_youtube url=”https://youtu.be/9my0gNEQszw” title=”Gynecomastia – All you need to know”]
To consult an expert Medfin surgeon near you, please call us on 7026200200. You can also WhatsApp us on 7406557599 (click here to initiate a whatsapp chat).
CATEGORIES
- ACL Reconstruction
- Anal Fissures
- Anal Fistula
- Appendicitis
- ASK A DOCTOR
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Breast Lump Excision
- Cataract
- Circumcision
- Conditions & Diseases
- Cosmetology
- Covid-19
- Cure
- Endocrinology
- ENGLISH VIDEOS
- Eye Care
- Gallstones
- General Surgeries
- Government Schemes
- Gynaecology
- Gynecomastia
- Gynecomastia
- Health
- Health Insurance
- Hernia
- hindi
- Hip Arthoscopy
- Hip Replacement
- Hip Replacement Surgery
- Hydrocele
- Kannada
- Kidney Stones
- Knee Arthroscopic
- Laparoscopic
- LASER
- Latest Treatments
- Lifestyle
- Liposuction
- Medfin Stories
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedic
- Paraphimosis
- Patient Testimonials
- PCL Reconstruction
- Phimosis
- Piles (Hemorrhoids)
- Pilonidal Sinus
- Proctology
- Prostate Artery Embolization
- Rhinoplasty
- Second Opinion
- Total Knee Replacement
- Uncategorised
- Urology
- uterine artery embolization
- Uterine Fibroids
- Varicocele
- Varicose Veins
- Vascular
- VIDEOS






